DVT: Symptoms, Medications & Leg Treatments
Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis, often abbreviated as DVT, is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot develops in the deep veins of the body, most commonly in the legs. Recognizing the early stage DVT symptoms is crucial for timely treatment and prevention of complications such as pulmonary embolism. Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis in the leg may include swelling, pain, and redness. These symptoms can vary in intensity, which is why medical consultation is recommended as soon as they are noticed. A comprehensive understanding of DVT can aid in effective management and prevention of further health issues.
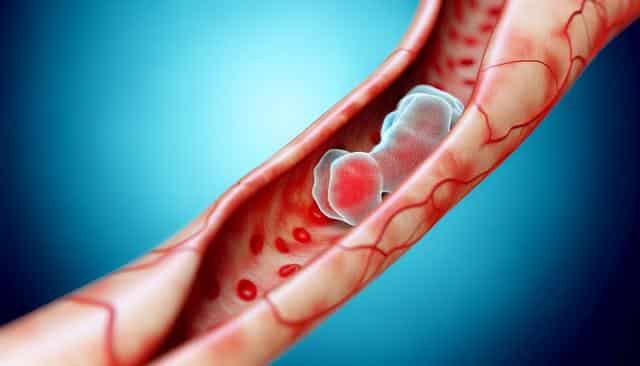
Identifying Symptoms and Risk Factors
Detecting symptoms of deep vein thrombosis in the leg early is essential for effective treatment and management. Common indicators include leg swelling, cramps, and a feeling of warmth in the affected area. Moreover, visible veins and a change in skin color can also signal the presence of a blood clot. However, not every individual will experience these symptoms, and some may encounter no symptoms at all, making regular check-ups crucial for those at risk. Several factors increase the likelihood of developing DVT, such as prolonged immobilization, recent surgery, or a family history of blood clots. Understanding these risks can guide preventive measures and prompt action when any symptoms arise.
Treatment Options for DVT
Once diagnosed, the treatment for DVTs involves several strategies aimed at preventing clot growth and reducing symptoms. Medication is often the first line of treatment, with blood thinners being amongst the most commonly prescribed options. These medications help in dissolving existing clots and preventing new ones from forming, significantly reducing the risk of pulmonary embolism. In some cases, deep thrombosis treatment may also involve the use of compression stockings, which help relieve pain and swelling by improving blood flow in the legs. Surgical interventions may be considered when medications and compression therapy do not yield desired results, highlighting the tailored approach required in managing DVT effectively.
Role of Medication in Managing DVT
Deep vein thrombosis medication plays a pivotal role in the management and treatment of the condition. Blood thinning medicines, also known as anticoagulants, are at the forefront of medical treatment, designed to prevent the existing clot from enlarging and to reduce the risk of new clot formation. Commonly prescribed medicines for blood clots in legs include warfarin and heparin, each having specific dosage and monitoring requirements to ensure efficacy and safety. Patients are often required to regularly undergo blood tests to monitor the effectiveness of these medications and to prevent any potential side effects. In some cases, newer medications, known as direct oral anticoagulants, might be recommended for their ease of use and predictable performance.
Preventing Complications and Maintaining Health
Prevention and education are key components in the battle against DVT and its complications. Staying active, especially during long periods of immobility such as flights or desk jobs, can significantly lower the risk. Incorporating activities like leg exercises and regular walking into the daily routine can boost circulation, thus reducing the chance of clot formation. Patients with previous incidents of DVT or significant risk factors may be advised to continue taking preventive medication or wearing compression garments. Building awareness of the symptoms and risk factors can empower individuals to seek early intervention and adopt lifestyle changes that minimize the risk of future occurrences. By maintaining these preventive strategies, individuals can manage their health more effectively and reduce the likelihood of complications arising from deep vein thrombosis.
